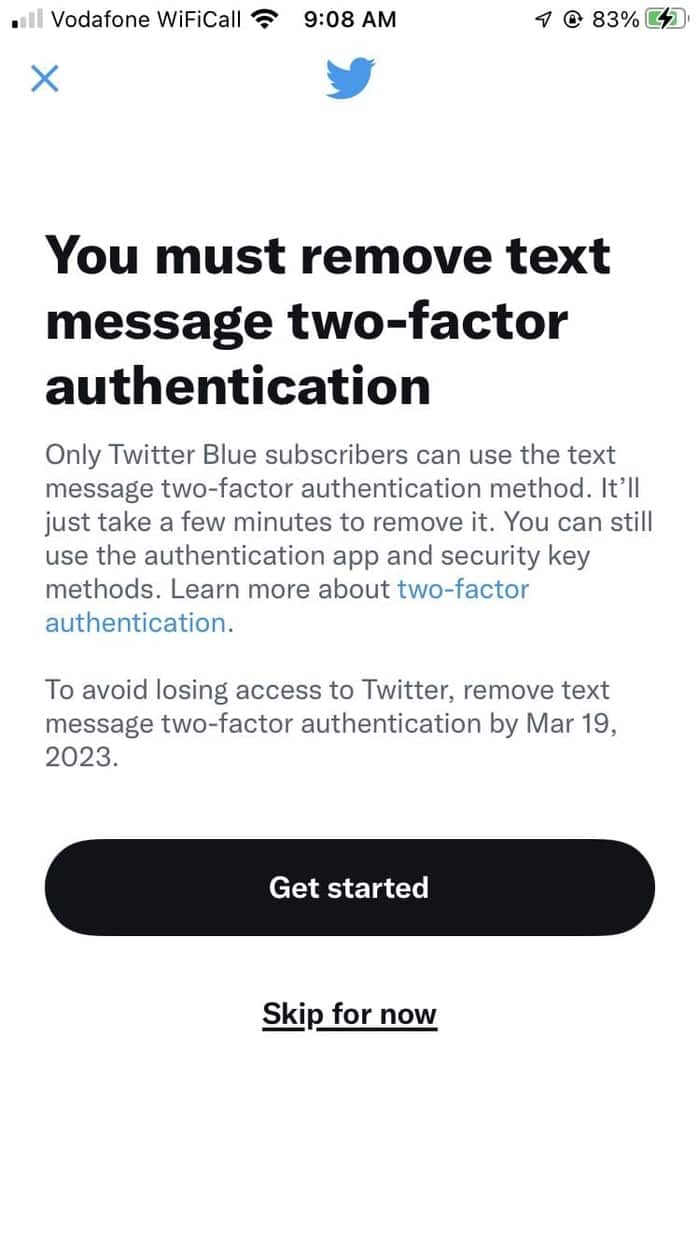
Many Twitter users have been presented with a message telling them that SMS-based two-factor authentication (2FA) will be removed next month.
According to Twitter, only subscribers to its premium Twitter Blue service will be able to use text message-based 2FA to protect their accounts.
Frankly, there’s a lot to unpack here.
First, let’s explain why 2FA is a good thing for your account security.
2FA adds an additional step during the login process to services like Twitter. Rather than just needing your username and password, sites protected by 2FA also ask you to enter a six digit verification code – which changes every 30 seconds or so.
The idea is that even if a hacker has managed to find out what your password is, they don’t know your 2FA code. That’s because the code is sent to you via SMS, or generated by an app on your phone, or possibly even on a hardware key.
There are still ways to get around 2FA security, but it requires a lot more effort by anyone trying to break into your account, and chances are that most attackers simply wouldn’t bother going the extra mile and find an easier target instead.
One problem with SMS-based 2FA (where the token is sent via text message) is that in the past fraudsters have managed to launch a so-called “SIM Swap” attack.
A SIM swap attack is when a scammer manages to trick the customer service staff of a cellphone provider into giving them control of someone else’s phone number. Sometimes this is done by a fraudster reciting personal information about their target to the company, tricking them into believing they are someone they’re not. When an online account – such as Twitter – subsequently sends its authentication token to the user’s phone number via SMS it ends up in the hands of the criminal.
Victims of SIM swap attacks in the past have included former Twitter boss Jack Dorsey, who had his Twitter account hijacked in 2019.
This is the reason why organizations like the US National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) stopped recommending SMS-based 2FA years agoand why it continues to be my least favorite form of 2FA.
But I still argue that SMS-based 2FA is better than no 2FA at all.
And my worry about Twitter’s decision to remove text message two-factor authentication is that it will leave many of its users worse protected than before. Because many folks will simply follow Twitter’s advice to turn it off, and not swap over to an alternative form of 2FA.
Twitter’s motives are not to better secure its user base. This is being done by Twitter in a desperate drive to save itself money, not to improve the security of its users.
If it thinks it will sell more Twitter Blue subscriptions that seems optimistic in my mind. I worry that positioning SMS-based 2FA as being only available to people prepared to pay a monthly subscription to Twitter, they may actually be sending out a false message that 2FA via text message is actually the safest version of 2FA.
Which it certainly is not.
Addendum
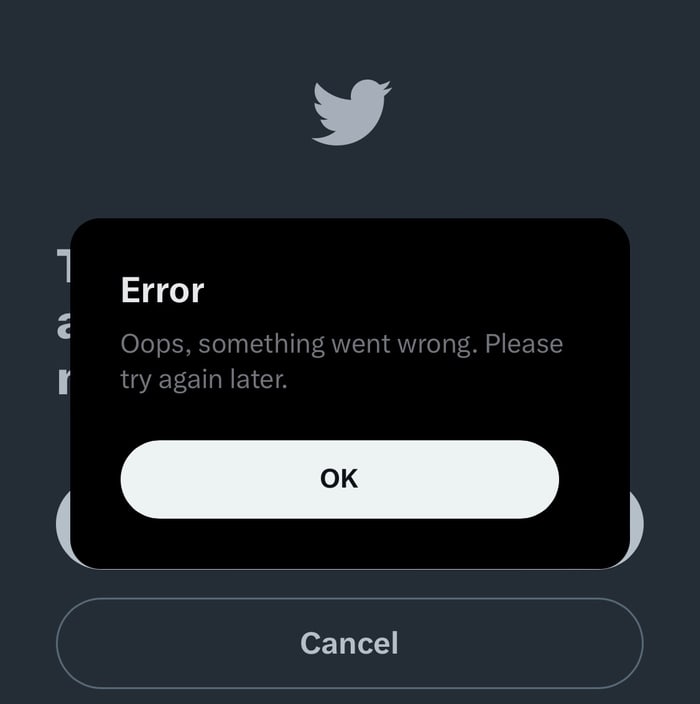
Under Elon Musk’s new rule (and amid huge layoffs within its engineering departments), Twitter appears to have predictably mucked up.
Users are reporting that when they attempt to disable text message 2FA as requested, they’re seeing the following message.
I’m not sure whether to laugh or cry…
Found this article interesting? Follow Graham Cluley on Twitter or Mastodon to read more of the exclusive content we post.